Chromic
Anodising
Highest corrosion protection & optimum adhesion for aluminium
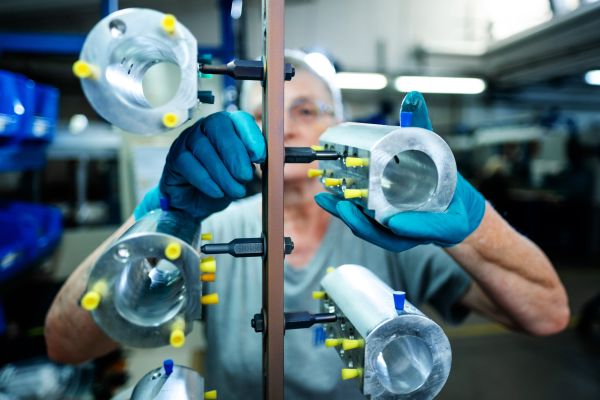
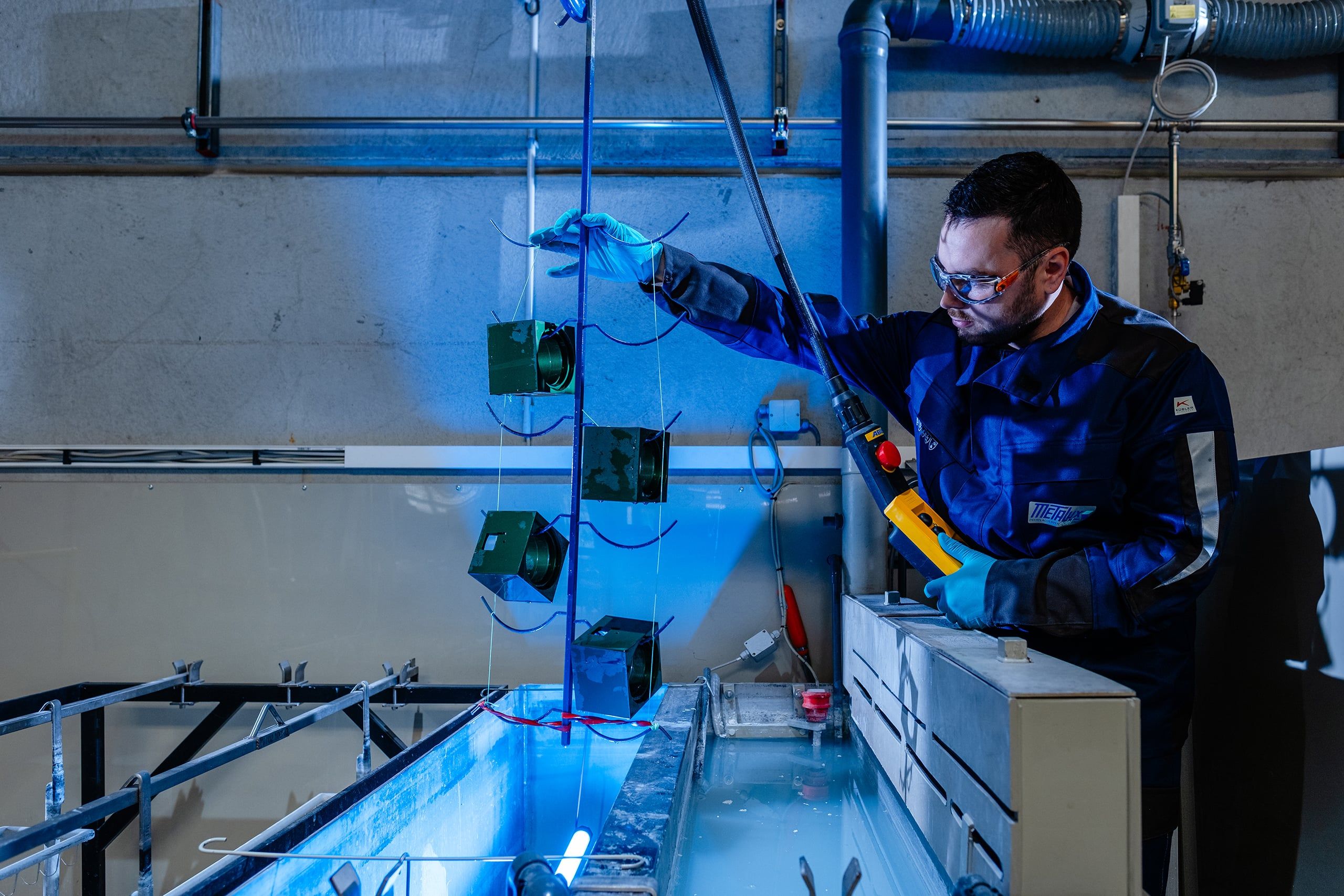
Chromic acid anodising is a special anodic oxidation process that is primarily used in aviation and other high-security areas. It is used where conventional anodising is not suitable due to fatigue strength and where the highest corrosion protection requirements must be met at the same time.
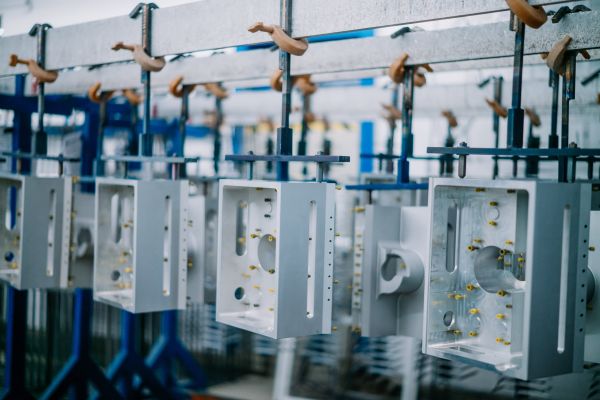
A particular advantage of this method is the excellent adhesion primer formation for subsequent painting or bonding, making it ideal for complex, further processed aluminium components.


Chromic acid anodising differs from other anodising processes due to its special process parameters. Factors such as current density, exposure time and temperature significantly influence the formation of the oxide layer.
Thanks to these unique properties, chromic acid anodising is indispensable in the aviation industry and is used wherever aluminium components need to remain mechanically flexible.
Uncompressed layers enable the best paint & adhesive adhesion
Reliably protects aluminium from environmental influences
Electrolyte residues do not lead to corrosion
Provides elasticity, but no mechanical resilience
Chromic acid anodised components are an essential component in aerospace technology, as the process offers decisive advantages:

No influence on the vibration resistance of the component

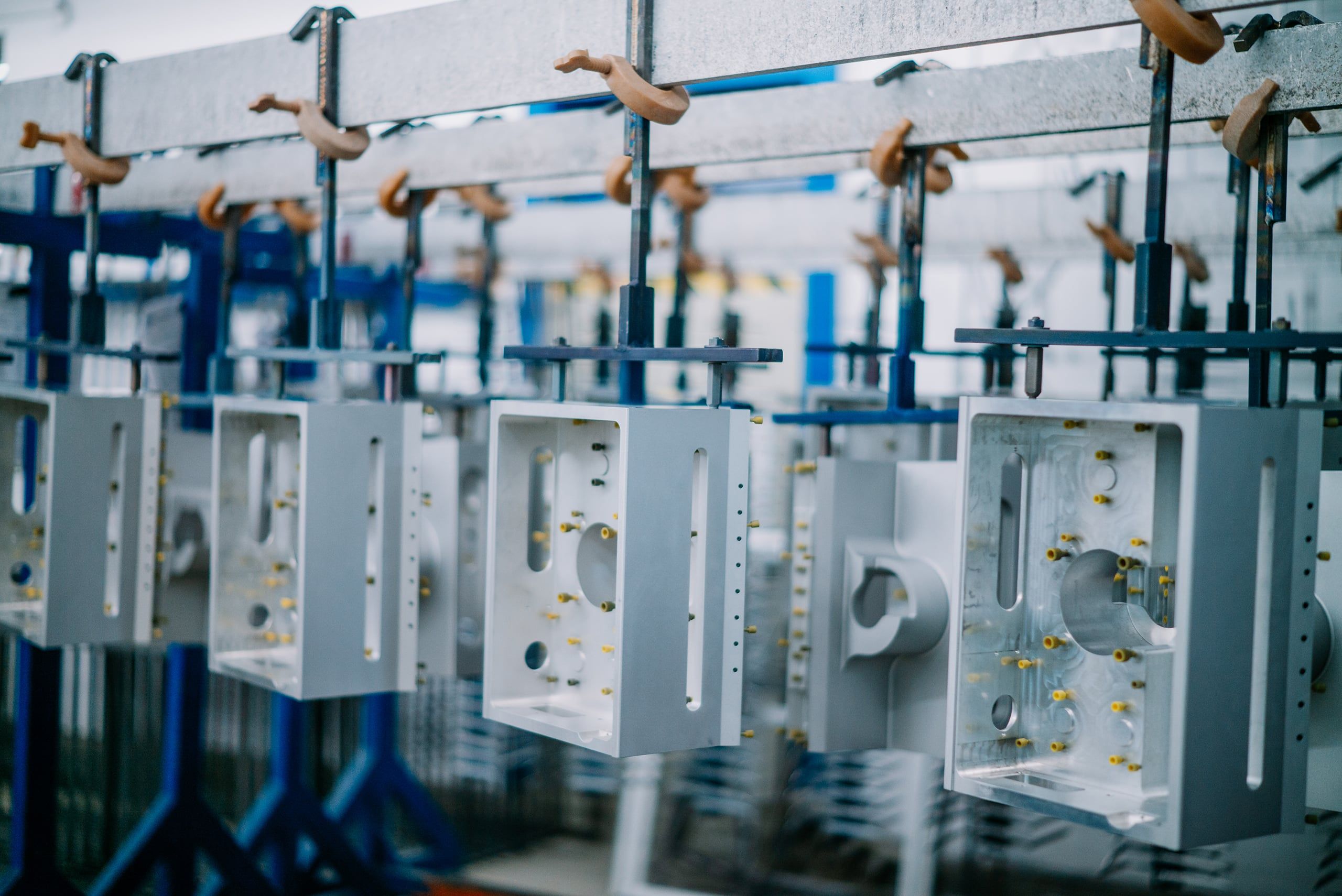
Perfect for complex structures & cavities

The anodised oxide layer makes fine material defects visible

Perfect primer without additional compaction

Kein Einfluss auf die Schwingfestigkeit des Bauteils

Perfekt für komplexe Strukturen & Hohlräume

Die anodische Oxidschicht macht feine Materialfehler sichtbar

Perfekter Haftgrund ohne zusätzliche Verdichtung
These properties mean that chromic acid anodising is used for aircraft structures, load-bearing aluminium parts and safety-critical components, among other things.
As the process makes capillary effects in the surface visible, it is also used for crack testing of safety-critical components.
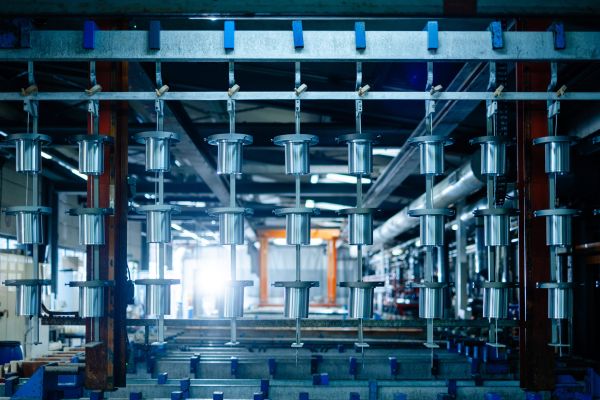
The layer formation in chromic acid anodising differs from classic sulphuric acid anodising:
1/3 to the outside, 2/3 to the inside
1-5 μm depending on the alloy
No additional brittleness of the components
Grey to greenish, depending on the silicon content of the alloy
Chromic acid anodised aluminium surfaces offer a range of unique properties:
In principle, many aluminium alloys can be chromic acid anodised. There are restrictions for:

Suitability must be checked individually

Not ideal for the process

Eignung muss individuell geprüft werden

Nicht optimal für das Verfahren
Für Klebe- & Lackanwendungen darf die Schicht nicht verdichtet werden, um die optimale Haftung zu gewährleisten.
Chromic acid anodising produces thinner, more elastic layers with better adhesive properties, while sulphuric acid anodising forms harder & thicker layers.
No, the layered structure does not allow for intensive colouring. The natural colour varies between grey and green.
The process offers perfect corrosion protection and does not impair fatigue strength, which is crucial for aircraft components.
Typical layer thicknesses are between 1-5 μm, depending on the alloy.
The process is subject to strict environmental regulations, particularly when handling chromic acid. Modern waste water and recycling plants minimise the environmental impact.